Lesson 11: Positive Change and Recovery
Attention
Learning Outcomes
Upon completion of this lesson's material, students will be able to:
- Identify the Stages of Change
- Identify strategies that help facilitate change.
Teaching
Read Chapter 20
Recovery Model
- Seeing problems and illness as only PART of the person
- Client is a PARTNER
- Developing a trustworthy relationship
- Collaborating on goals that are important to the CLIENT
- Support and Encouragement
- Belief that people can change
- Providing services that help the CLIENT make change
Discouraging Recovery
- Making decisions without consulting the client
- Set goals without the client input
- Demean clients
- Act as if clients are less competent than they are
What is CHANGE?
- Commitment and hard work
- Immediate improvments?
- Long-term alterations?
- Change of habits?
- Accepting diagnosis?
- Accepting things that can/cannot change?
What keeps people where they are?
- Fear
- Uncertainty
- Stubbornness
- Denial
- Lack of confidence
- Lack of hope
- Inabiity to see a different future
How to Motivate and Encourage (Motivational Counseling)
- Meet the client where they are
- See the client's strengths
- Accurately assess the clients ambivalence
- Appreciate every effort
- Never lose sight of potential
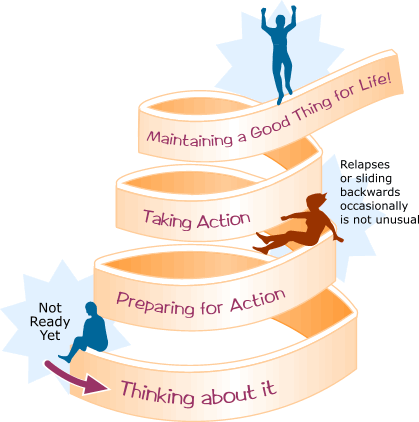
Stages of Change
- Stage 1: Pre-contemplation
- The client is not ready for change and probably not thinking about it
- INTERVENTION
- Focus on reviewing consequences of actions
- Identify and empower opportunities that the individual has to make change in their lives
- Work primarily with motivations
- Stage 2: Contemplation
- The client is ready to explore changes but not ready to commit
- INTERVENTION
- Explore fears
- Explore "what if" scenarios
- Identifying barriers
- Stage 3: Developing a Plan
- The client is ready to change, but needs a plan
- INTERVENTION
- Actions address barriers
- Specific steps and outcomes
- Timeframe
- Stage 4: Implementing the Plan
- The client will be uncertain, but will actually change habits, behaviors, or thinking
- INTERVENTION
- Schedule follow ups on plan
- Support mechanisms for "crisis" situations
- Recording results for progress
- Stage 5: Maintaining Changes
- The client wants the changes to be permanent. Sometimes there are still obstacles
- INTERVENTION
- Long term lifestyle choices
- Ongoing "natural" supports
- Celbration and generalization
- Relapse
- Client is unable to sustain the change over the long term and may return to the old ways
- INTERVENTION
- Emotional support
- Identify barriers and triggers
- Assess new Stage of Change
Assessment
In Class Group Work
Read through the five example on p. 339-340. Which person do you think would be the least likely to make change? Why? What strategies would you use if that person were your client?
Lesson 11 Quiz
Refer to Exercises: Helping People Change on page 339. (Make sure you review the INTERVENTIONS when reviewing these case studies to help determine which stage the person is in.)
- What stage of change is Kelly in?
- What stage of change is Marlo in?
- What stage of change is Ben in?
- What stage of change is Elmer in?
- What stage of change is Elise in?