Lesson 4: Prenatal Development, Genetics, and Critical Periods
Attention
To view this video directly in YouTube click HERE
In this video we see the processes involved in the fertilization of the human egg and the development of the multicultural mass that imbeds itself in the uterine wall for the duration of a pregnancy.
The start of human life...
To view this video directly in YouTube click HERE
This video shows the development of the fetus...right until just before birth
Learning Outcomes
Upon completion of this lesson's material, students will be able to:
- Identify critical psychological development that occurs while a fetus develops
- Identify specific genetic abnormalities that occur while a fetus is developing
- Identify key critical periods related to neurological development
Teaching
Behavioral States in a Fetus
State 1F: Quiet sleep. The fetus exhibits occasional startles, no eye movements, and a stable fetal heart rate. This occurrence of state increases from about 15% at 36weeks of gestation to 32% at 38weeks and 38% at term.
State 2F: Active sleep. This state is characterized by frequent and periodic gross body movements, eye movements are present and the fetal heart rate shows frequent accelerations in association with movement. This is the most commonly occurring state, being observed around 42–48% of time in the fetus.
State 3F: Quiet awake. No gross body movements are observed, eye movements are present, and the fetal heart rate shows no accelerations and has a wider oscillation bandwidth than in state 1F. This is a rare state to observe, as it occurs only briefly. In fact its occurrence is usually represented by number of occurrences rather than as a percentage of time
State 4F: Active awake. In this state the fetus exhibits continual activity, eye movements are present, the fetal heart rate is unstable, and tachycardia (increased pulse rate) is present. This state occurs about 6–7% of the time between 36 and 38 weeks of gestation increasing to 9% just before birth, around 40 weeks of gestation.
Fetal Senses
Hearing
Fetus responds to sound from 22-24 weeks by moving around. The environment is rather noisy with mom's heartbeat, breathing, and digestive system.
This video is for a company that sells CDs of Womb Sounds but it gives you an idea as to what babies hear in their mom!
Taste and Smell
Difficult to separate in the womb. Fetus is able to distinguish between sweet and noxious substances added to the amniotic fluid. Increased swallowing with sweet and decreased swallowing with noxious.
Pain
Neural pathways for pain are formed at 26 weeks.
Temperature
Highly regulated by the womb, but the baby can react to a warm bath
Touch
Touch is the first sense to develop...about 8 weeks. At 14 weeks the whole body is sensitive to touch.
Vision
Least likely to develop...it is dark in there. But, by 26 weeks the fetus can react to a bright light.
Fetal Learning
- Habituation---will not react as much to repeated sounds
- Mother's Voice
- Music they have heard prenatally is preferred
Genetic Abnormalities
This is an image of what chromosomes look like under high magnification! To think that all that information is stored in these things!
Here is a short list of basic terms you should look up and understand to get the most out of this chapter:
- Genes
- Chromosomes
- Autosomes
- Sex Chromosomes
- Genotype
- Phenotype
- Dominant and Recessive Genes
- Abnormal Chromosomes and Disorders
The Link Between Behavior and Genetics
- The behavioral consequences of genetic instructions depend on the environment in which those instructions occur
- What if Michael Jordan was born in a country that did not have "Basketball"? What would he be?
- Heredity and environment interact dynamically (back and forth, they both influence the other) throughout development
- This answers the Nature vs. Nurture question...the answer is BOTH!
- Genes can influence the kinds of environment to which a person is exposed
- Consider traits such as attractiveness, height, weight, strength, intelligence, etc...all of which are highly influenced by heredity...what doors do these open? What doors do these close?
- Environmental influences typically make children within a family different
- No matter what each child is raised different from the others! Those of you with siblings know exactly what I'm talking about!
Million Dollar Question...
Since we use a lot of resources to manipulate the ENVIRONMENTAL influence in a child's life (school, family, family services, nutrition programs, early childhood intervention programs, summer camp, etc. etc.)...and we know that environment only accounts for PART of the influences that effect change...why not invest in manipulating the GENETICS!!!
Visit the online home of the Human Genome Project
In particular...explore the page they have on the Ethical concerns of their work...pretty impressive...they understand what they are getting into!
Want to get DEEP into the controversy! Visit this site: http://infotrac.galegroup.com/itweb/fair94921 and type "lunder" to get access to KVCC's subscription to "Opposing Viewpoints"! Search "Genetics" and read some really good opposing articles on the subject!
Sometimes things do not go as planned. Click HERE for a great website on genetic abnormalities that occur
- Genetic Disorder
- Chromosomal Disorder
Prenatal Development and Critical Periods
Click HERE to download a document that reviews many aspects of Prenatal Development. This document was created by Kimberly Carey, CNM, MS, Certified Nurse Midwife.
Take this Prenatal Development and Childbirth quiz...which covers a lot of what is above...and some additional information as well! (It is ungraded, but see how you do!)
Critical Periods
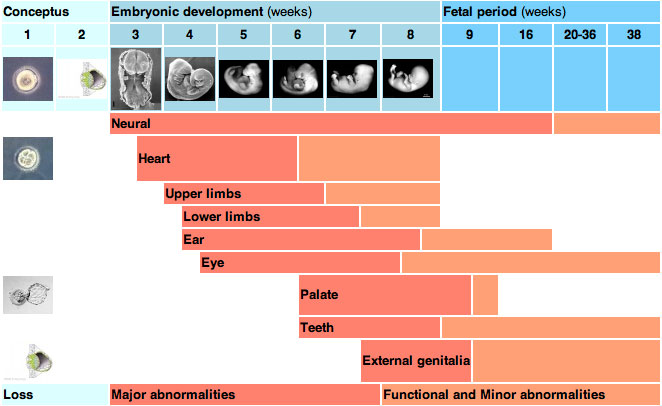
Development of specific parts of the body occur during specific times. Teratogens, which is the word for anything that can negatively effect this process, will effect the processes that are undergoing critical development. This is called the Threshold Effect.
For example: If a teratogen is present at 3 weeks it may effect the neural and heart development...and the loss could be "major abnormalities"
Assessment
Lesson 4 Quiz
- A friend approaches you and tells you that while at a party she was slipped a drug in her drink. She is unsure what the drug is, but she is in her 9th week of pregnancy. She is concerned that the drug may effect the development of her unborn child. Utilizing the chart on critical periods in the lesson identify the potential impacts that this mystery drug may have on the child. Be sure to identify each area that is impacted and if the impact is potentially a "major abnormality" or a "Functional and Minor Abnormality".