Lesson 23: Family Structure
Attention

Families come in all shapes and configurations
Learning Outcomes
Upon completion of this lesson's material, students will be able to:
- Identify similarities and differences between families
- Describe diversity in families in the US
Teaching
Family
In Sociology we refer to the family as a "social institution" and you have likely heard that term before. As such we can apply all our tools of analysis to an analysis of the family.
Functions of the Family
- Sexual Regulation
- Reproduction and Socialization
- Economic Security
- Emotional Support
- Social Placement
Consider this: The primary function of the family is to socialize the next generation. What have you learned from your family?
Marriage
- Cultural Universal
- Legal
- Norms, Values, and Expectations
From one viewpoint a marriage is a behavior contract binding individuals into a set of social and psychological expectations
How Families Differ
- Nuclear Family and Extended Family
- Geography
- Authority and Power
- Courtship Patterns
- Monogamy and Polygamy
- Cohabitation
- One- vs. Two Incomes
- Gay and Lesbian Families (Redefinition of Marriage)
Divorce
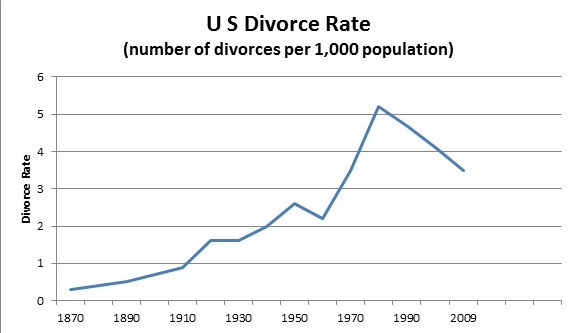
- Divorce during the first 9 years is about 42%
- Divorce after 50 years of marriage is about 1%
Assessment
Possible Class Discussion A
Select one of the areas related to how families differ that is important to you. Do some research on the web and find at least two interesting aspects or statistics related to this topic. Discuss how this information relates to the FUNCTION of the family.
Possible Class Discussion B
Despite the decreasing number of divorces going on, why do we have the perspective that the "Institution of the Family" is in decline.