Lesson 12: Attachment
Attention
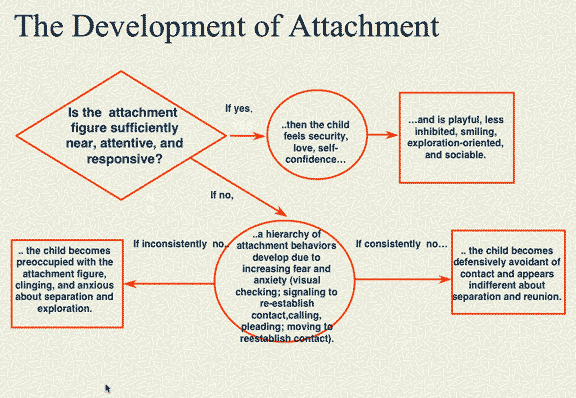
This graphic does a pretty good job about outlining the development of attachment
Learning Outcomes
Upon completion of this lesson's material, students will be able to:
- Identify the consequences of successful secure attachment on development later in life.
Teaching
Attachment
Attachment is an enduring socioemotional relationship between infants and their caregivers.
- Preattachment (birth to 6-8 weeks)
- Attachment in the Making (6-8 weeks to 6-8 months)
- True Attachment (6-8 months to 18 months)
- Reciprocal Relationships (18 months on)
Click HERE to see this on YouTube directly
This video provides a nice overview of the importance that Attachment Theory has had on the field of Developmental Psychology
Click HERE to see this on YouTube directly
Although this video has some strange editing in it, there is an excellent clip about the "Strange Situation" experimental method developed by Ainsworth
Forms of Attachment
Based on the observed results of children's behavior in the Strange Situation experiment, Ainsworth described 4 types of Attachment:
Secure Attachment---The baby may or may not cry when the mother leaves, but when she returns the baby wants to be with her, and if the baby is crying it stops.
Avoidant Attachment---The baby is not upset when the mother leaves and, when she returns, may ignore her by looking or turning away.
Resistant Attachment---The baby is upset when the mother leaves, and it remains upset ore even angry when she returns and is difficult to console
Disorganized Attachment---The baby seems confused when the mother leaves and when she returns, as if not really understanding what's happening.
Internal Working Model
The baby develops an internal working model of the world. (This is a fundamental component of the Trust vs. Mistrust stage we have discussed already). But, what about working moms and families? How is daycare impacting the relationship between children and their caregivers?
Click HERE to review a study that discusses how parents are actually spending MORE time with their kids (at least when the study was done). How does having a stay-home parent impact development?
Consequences
What are the consequences of successful attachment experiences as an infant?
What about adopted kids? Neglect? Abuse?
Assessment
There is no Assessment for this Lesson