Lesson 11: Residential Services and Housing
Attention
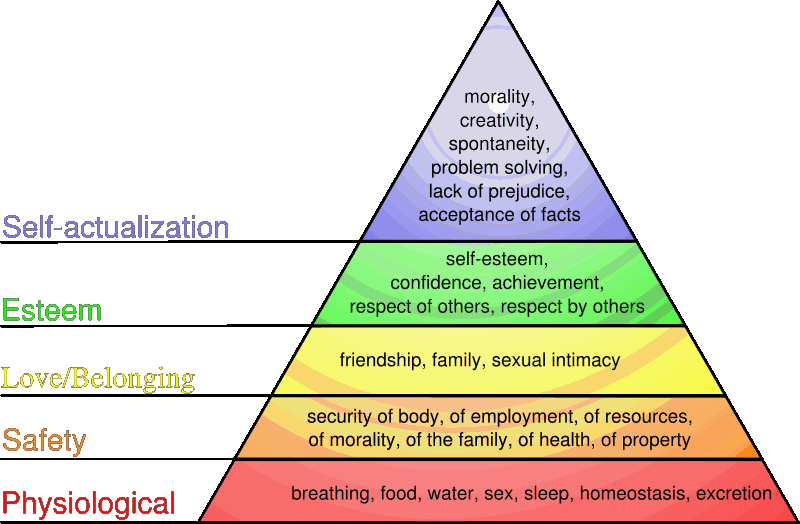
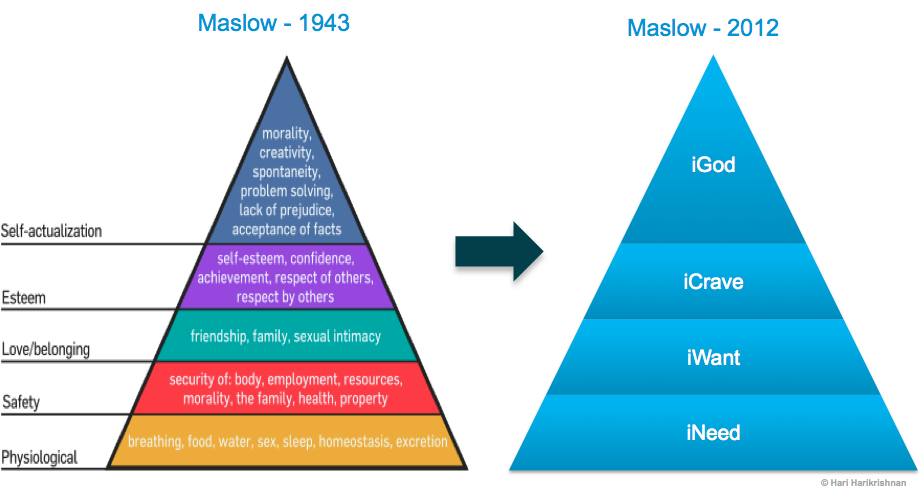
Consider this graphic...which depicts the hierarchy of needs as described by Maslow's theory...where does housing fit into this? How important is it to have a "place to lay your head"?

A link to this optional book on Maslow is available in the Optional Course Materials in the iTunes U class!
Learning Outcomes
Upon completion of this lesson's material, students will be able to:
- Reflect on the change from transitional housing to supported housing and apartments.
- Consider how changes in housing services reflect the growing influence of the PSR philosophy
Teaching
Housing
Two “financial” reasons why housing is difficult
- Affordable housing is less available
- Cuts in funding for federal assisted low-income housing
Stigma
How do landlords, fellow tenants, neighbors, etc feel about having persons with mental illness next door?
- Safety
- Property values
- Exclusion from “community”
Systemic Issues
- Residential treatment vs. permanent housing
- Extended hospital stays simply because of lack of housing
- “Burden” on families who are often ill-prepared
History
The history of housing for persons with mental illnes is essentially the same as the history of mental health treatement itself.
- In old days we kept individuals at home. Later they were often located to boarding houses and other care facilities for the "feeble minded"
- As the local resources became overwhelmed and the state government began to become powerful the large institutions wer built. Individuals were often very far from home living in state run institutions such as Augusta Mental Health Institutue (now called Riverview), Bangor Mental Health Institute, and Pineland Institute (now closed).
- With the advent of Supplemental Security Income, Medicaid, and the Mental Health Centers (all legislation under Kennedy), moving into the community began to be a viable option. (Medications are often credited with creating deinstitutionalization but far more it was the impact of SSI.)
Various services and housing options have been attempted over the years. Individuals options were often irratic and unstable.
- 1/4 way Houses
- Half-way Houses
- 3/4 way Houses
- Supported Apartments
- All of these continue to exist for some folks.
Group Homes and Halfway Houses
- Linear continuum Paradim (as you got better you can move to a place of more independence...not exactly the best motivator..."Go ahead, get better and we will kick you out!")
- Transitional Housing
Supported Housing
- Avoids "placement" stigma since the housing is "normal"
- PSR oriented
- Family may be involved
- Normalization
- ADL focus (Activities of Daily Living)
- Formal and Informal Support
- Advocacy
Independent Living Movement
- Recognition that it is not something “internal” that makes someone disabled
- De-medicalizing of the issues
- Persons with disabilities have a right to self-determination
- Persons with disabilities can become experts in their own care
Independent Living Centers
- Grassroots
- Advocacy
- Support
- Training
For a few years I used to work for Maine Independent Living Services, one of the first Independent Living Centers in the US. Sadly it is closed now.
My experience with IL was very positive. Individuals with disability helping others with disabilities. The services were particularly good when the worker could relate to what the individual was going through. Alpha-One, the remaining IL center in Maine, only hires individuals with a personal history of disability.
Assessment
Lesson 11 Quiz
- Reflect on the change from transitional housing to supported housing and apartments. In what ways, citing the specific values of PSR, does this method of service delivery benefit clients?
Lesson 11 Discussion
In this discussion I would like you to reflect on this brief article and the iPad itself (and our application of it in the m-Learning Program)