Lesson 11: Positive Change and Recovery
Attention
Learning Outcomes
Upon completion of this lesson's material, students will be able to:
- Identify the potential barriers to change
- Identify how the Stages of Change apply to personal change processes
Teaching
Recovery Model
- Seeing problems and illness as only PART of the person
- Client is a PARTNER
- Developing a trustworthy relationship
- Collaborating on goals that are important to the CLIENT
- Support and Encouragement
- Belief that people can change
- Providing services that help the CLIENT make change
- Read: NASW Practice Snapshot: The Mental Health Recovery Model
Discouraging Recovery
- Making decisions without consulting the client
- Set goals without the client input
- Demean clients
- Act as if clients are less competent than they are
What is CHANGE?
- Commitment and hard work
- Immediate improvments?
- Long-term alterations?
- Change of habits?
- Accepting diagnosis?
- Accepting things that can/cannot change?
What keeps people where they are?
- Fear
- Uncertainty
- Stubbornness
- Denial
- Lack of confidence
- Lack of hope
- Inabiity to see a different future
- Addition thoughts on What keeps me from changing?
How to Motivate and Encourage (Motivational Counseling)
- Meet the client where they are
- See the client's strengths
- Accurately assess the clients ambivalence
- Appreciate every effort
- Never lose sight of potential
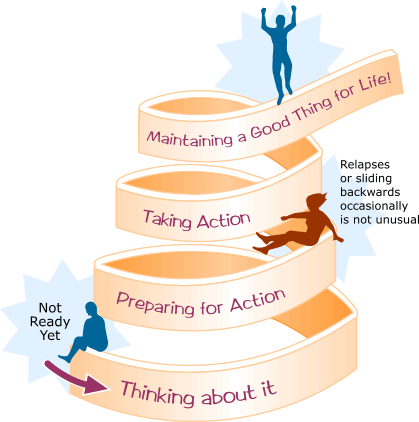
Stages of Change
- Stage 1: Pre-contemplation
- The client is not ready for change and probably not thinking about it
- INTERVENTION
- Focus on reviewing consequences of actions
- Identify and empower opportunities that the individual has to make change in their lives
- Work primarily with motivations
- Stage 2: Contemplation
- The client is ready to explore changes but not ready to commit
- INTERVENTION
- Explore fears
- Explore "what if" scenarios
- Identifying barriers
- Stage 3: Developing a Plan
- The client is ready to change, but needs a plan
- INTERVENTION
- Actions address barriers
- Specific steps and outcomes
- Timeframe
- Stage 4: Implementing the Plan
- The client will be uncertain, but will actually change habits, behaviors, or thinking
- INTERVENTION
- Schedule follow ups on plan
- Support mechanisms for "crisis" situations
- Recording results for progress
- Stage 5: Maintaining Changes
- The client wants the changes to be permanent. Sometimes there are still obstacles
- INTERVENTION
- Long term lifestyle choices
- Ongoing "natural" supports
- Celbration and generalization
- Relapse
- Client is unable to sustain the change over the long term and may return to the old ways
- INTERVENTION
- Emotional support
- Identify barriers and triggers
- Assess new Stage of Change
Assessment
Possible Class Discussion
Many times we see our clients' resistance to change as being "manipulative" or "lazy"...but usually there are many contributing factors. Consdider the following potential barriers to change:
- Fear
- Uncertainty
- Stubbornness
- Denial
- Lack of confidence
- Lack of hope
- Inabiity to see a different future
Because we tend to see our own personalities reflected in others' behavior, discuss which of these you might be more likely to consider because it is something YOU would do...so you can see that others could do it as well.
For example: I might clearly see that someone is not doing something because they are being stubborn...I can really relate to that! I can be very stubborn myself, particularly if I see my performance as reflective of who I am.
Lesson 11 Quiz
- Identify a specific are in your own life that entailed a personal change that was challenging. Tell your story in a way that outlines how you made your way through a number of the "Stages of Change"