Lesson 17: Government and Politics
Attention
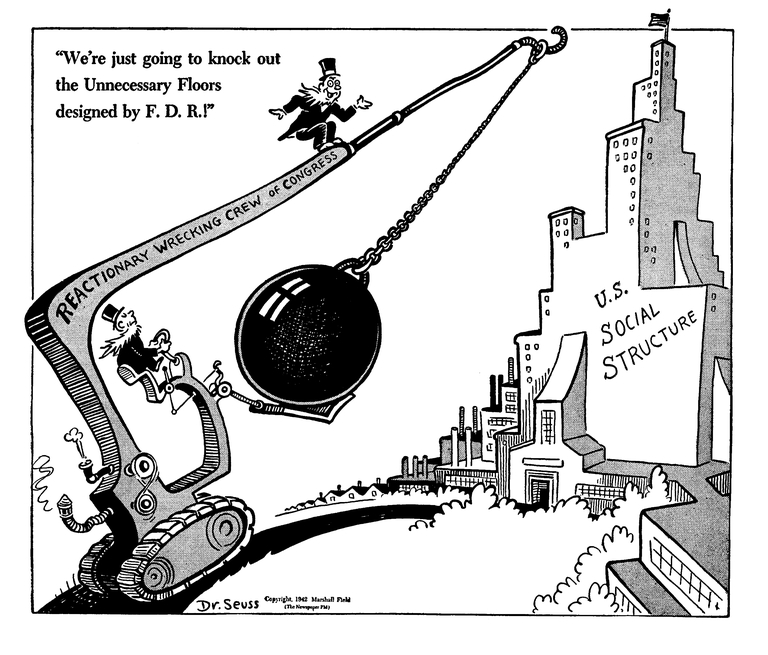
And you thought that Dr. Seuss only drew cartoons for kids! Political cartoons are a mainstay in American society.
This particular one critiques the congress for haphazardly deconstructing what Franklin D. Roosevelt had done during his administration.
Learning Outcomes
Upon completion of this lesson's material, students will be able to:
- Differentiate between power and authority.
- Compare different forms of government and provide real-life examples of each.
- Discuss viewpoints on if the United States is actually an Oligarchy.
- Discuss the history and purpose of the Electoral College.
Teaching
This is not Political Science
While the field of Political Science is closely aligned with Sociology, their approach to a study of Politics is different. Political Science seeks to understand the distribution of power within different government structures (also of importance to Sociology) whereas Sociology is more concerned with how that political structure impacts society and people in it.
Essentially, we group our political systems in with other Agents of Socialization, including Family, the Media, Schools, Religious Institutions, etc.
Power vs. Authority
While these two concepts are related to one another they are starkly different. Power is the ability that someone has to exercise their will over someone else. Authority is accepted or legitimate power that people agree to follow.
We can see these concepts in many aspects of our society. As a teacher, for example, I have legitimate authority to dictate the content of the course and the assignments...however, I don't have the power to MAKE someone complete the assignments.
Consider different people in our society that have specific power and authority in different circumstances.
Forms of Government
The exercise of power and authority (mixes of each) manifests in various forms of government around the world and across history. Consider the following:
- Monarchy - a single person rules until they die or abdicate the throne.
- Absolute Monarchy
- Constitutional Monarchy
- Oligarchy - a small elite group of individuals rule.
- Dictatorship - power is held by a single individuals and that person holds absolute power.
- Democracy - strives to provide all individuals with an equal voice.
Notice that we have not included terms such as Socialist or Communist...these are actually not really forms of government, but economic models...we will discuss those later.
The Electoral College
As I write this Lesson, we are just days after the election of Donald Trump as the 45th President of the United States. While this came as a surprise to many, the fact remains: he won the election.
As happens nearly every election, there is concern and confusion about the system of voting that we have called the Electoral College. This system, largely misunderstood was not created to cause confusion and make elections more complicated but to prevent simple majorities from exercising complete power over elections, to engage politicians in coalition building, and to prevent voter fraud.
Here is a little video about the Electoral College
Assessment
The Online Discussions are for students who are taking Online and Hybrid versions of this class. Your Instructor will inform you if you have to pay attention to these...otherwise you can ignore them.
Lesson 17 Discussion A
Based on your understanding of the different forms of government, discuss if the United States is actually an Oligarchy rather than a Democracy.
Lesson 17 Discussion B
Review and discuss the video on the Electoral College. Do some additional web research as to arguments for and against this system.
Lesson 17 Quiz
- Compare and contrast the concepts of "power" and "authority".
- Select two forms of government from the list in the lesson, research it on the web, and provide a real-world example for each one. Please include a link to your web source in your answer.