Lesson 5: State of Maine Early Childhood Learning Guidelines
Attention
Learning Outcomes
Upon completion of this lesson's material, students will be able
- Students will discuss the components of the State of Maine Early Childhood Learning Guidelines.
- Students will discuss various indicators used as guidelines for preschool development.
- Students will discuss examples of observations used to determine a preschoolers understanding of specific indicators.
Teaching
The State of Maine Early Childhood Guidelines were created by many early childhood professionals for early care and education practitioners to use as a guide when teaching children three years old until they enter Kindergarten. These guidelines recognize that early childhood environments lay a critical foundation for a young child’s later success in school, work, citizenship and personal fulfillment.
The many individuals who were part of creating these guidelines looked at the development of the whole child and recognized that play, along with planning, guidance, support and follow-up are essential when promoting his development. A preschooler gains skill when given proper time to explore, are provided activities that are interesting, satisfying and respectful of his desire to touch, hear, see, smell and taste. By playing in a content-rich environment, a child will develop social and motor skills, begin to make sense of the world around them, and build a foundation to become capable, enthusiastic, engaged learners and responsible, healthy adults.
It is important to recognize that all children learn at their own pace. Some of the expectations provided in each domain will be appropriate for younger developmental stages while others will be more appropriate for children entering kindergarten.
One may wonder why we are learning about the Early Childhood Guidelines instead of Maine’s Early Learning and Development Standards. At the time of this writing, the Learning and Development Standards are still in Draft form. There have been no trainings offered to educators in regards to implementation and daily practical uses.
One can find the Early Learning and Development Standards at http://www.maine.gov/doe/publicpreschool/documents/Maine-ELDS.pdf if interested.
Purpose
The Early Childhood Learning Guidelines are intended to:
- Provide early childhood practitioners and families with guidance in designing learning environments, shape curriculum, lead professional development initiatives, build intentionality into teaching practices and support children’s learning at home.
- Be used as a guide for best practice
- Support and crosswalk into the State of Maine Learning Results used in K-12 public education
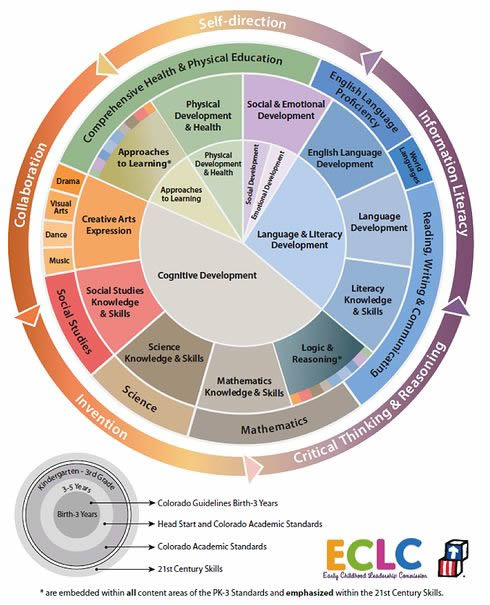
Structure
The Early Childhood learning Guidelines are organized in eight domains: Personal and Social Development. Approaches to Learning, Creative Arts, Early Language and Literacy, Health and Physical Education, Mathematics, Science and Social Studies. Within each domain there are Elements. Each Element has Indicators to clarify what children should know and be able to do upon entering Kindergarten. There is also a section that offers examples of what educators may observe as representation of the Indicators. The Guidelines have the following expected outcomes”
- Children have positive social relationships
- Children acquire and use knowledge and skills
- Children take action to meet their needs
The Whole Child
The Guidelines are broken down into Elements for the importance to assist in organization. Learning for young children cannot be isolated in the same manner. Learning occurs across all areas that it why it is important to look at the “whole” child. Children learn by constructing new knowledge from existing knowledge using their individual learning style. To learn more about The Whole Child Approach, please visit the following link: http://www.ascd.org/whole-child.aspx
Considerations when developing the Guidelines
- To provide goals and a continuum for what children should be able to do
- Expect educators to design environments and curriculum
- Assess and adapt teaching practices to meet the diverse needs of children based on each child’s way of attending, organizing information, communicating and interacting
- Provide children with a positive sense of personal well-being, developed through consistent caring relationships
- Develop social skills and behaviors that enable children to develop meaningful relationships with adults and peers
- Intentionally develop appropriate expectations and plans for what preschoolers should know and be able to do
- View preschoolers in the context of their family and culture
The Learning Guidelines are intended for families. Families can use the domains and indicators to guide their child’s development at home. With this being said, it is important to make sure that learning takes place in a fun, carefree manner not in a dictatorial, punishing, restrictive way.
It is important to realize the Learning Guidelines are not a curriculum. They can be deep-rooted in environment, curriculum, teaching practice, planning and assessment.
Personal and Social Development
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs suggests that all people need a safe and nurturing environment to achieve their full potential. This foundation enables children to become full contributing members of a community with a healthy sense of self and social skills to navigate a complex world. For more information regarding Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs, please go to the following link: http://www.simplypsychology.org/maslow.html
Personal and social skills gained in the early years through play, exploration and interactions enable a child to become a responsible, respectful member of a group while developing her own skills, interests and ambitions.
The Personal and Social Development Domain is broken down into three elements: Self Control, Self-Concept and Social Competence. Each element has several indicators and some examples you may observe children doing. To learn more about the developmental milestones of social and emotional development go to the following link: http://www.pbs.org/parents/childdevelopmenttracker/one/socialandemotionalgrowth.html
Approaches to Learning
Preschoolers are naturally curious and inquisitive. A child’s learning environment needs to be well-designed and intentionally builds on her interests, strengths, learning and knowledge. Educators need to encourage and facilitate play, stimulate her to explore, initiate, problem solve, extend her curiosity, and encourage her to ask multiple questions. Preschool teachers and family members need to work together to guide her in developing her attitude and skills to succeed in school and remain an active learner through her entire life.
Approaches to learning discuss Initiative and Curiosity as well as Persistence and Reflection. When looking over the indicators, it is important to adapt activities to each child’s physical, emotional, cognitive and social abilities. It is also important to look at the child’s culture and language in his home environment.
Watch this boy as he discovers the world around him:
After watching the video, refer back to the indicators. Which of the indicators could you use to describe what you watched?
Creative Arts
Creative Arts include music, visual arts, dance and theater which appeal to preschooler’s senses and are expressed through different materials and activities throughout their day. As an educator of these children, it is important to arrange an environment where art offers an outlet for emotional, creative and physical expression. The arts help children understand their world, acquire verbal and non-verbal abilities, problem solve, develop confidence, self-esteem, cooperation skills, discipline and self-motivation. The opportunities found in preschool to explore and manipulate materials lays a foundation for lifelong enjoyment of many expressive, analytical and developmental tools valuable in their daily lives. With all these educational values, it is most important to remember preschoolers should experience the arts as a source of enjoyment, expression and creativity.
The following video demonstrates how the arts can be part of a classroom daily:
Early Language and Literacy
Early Language and Literacy environments must provide hands-on exposure to books and language arts, creative expression through play and guided encouragement from adults to develop a child’s verbal and writing skills as well as a love of reading while increasing her vocabulary. She needs to become a critical thinker and effective communicator through various opportunities to explore and understand the basic elements of spoken and written language and the ways they are used.
Early Language and Literacy domain is divided into the following areas: Communicating and Listening, Book knowledge and Appreciation, Comprehension, Sounds in Spoken Language, Print Concepts, Alphabet Knowledge and Early Writing. These elements cover a wide variety of aspect in a child’s development.
The following video demonstrates a few strategies to guide a child’s phonological awareness:
Health and Physical Education
Health and Physical Education help preschoolers understand the benefits of safety, prevention, good hygiene and appropriate medical care. By providing health education, children become aware of the dimensions of good health: physical soundness and vigor, mental alertness and ability to concentrate, expressing emotions in a healthy way, resiliency and positive relations with others.
Healthy habits, Gross and Fine Motor Skills are covered in this section. The following link offers information to guide educators and families when preparing appropriate foods for preschoolers: http://kidshealth.org/parent/nutrition_center/healthy_eating/myplate.html
The following link offers an overview of Gross Motor Skills Development:
http://www.childdevelopment.com.au/areas-of-concern/gross-motor-physical-skills/184
Fine Motor Skill Development can be found at the following link:
http://www.childdevelopment.com.au/home/183
Mathematics
An early learning environment provides children with many rich opportunities to discover fundamental mathematical concepts and math’s relevance in daily life. Math activities include a variety of tools – blocks, scales, measuring cups and spoons, cubes and other hands-on materials. Educators need to intentionally help children understand the usefulness of those tools and how they encourage problem solving skills through purposeful activities which will lay a firm foundation for enjoyment and appreciation of mathematics for future successes.
Mathematics consists of Number and Number Sense, Shape and Size, Mathematical Decision-making and Patterns. In addition to working with these elements and indicators it is important to use math vocabulary when working with preschoolers. Mathematical language usage allows children to develop a firm foundation to aid in understanding of math concepts.
Please observe the following video to learn how to use math language to support learning:
Science
Preschoolers need many opportunities to explore experience and question to lay a foundation of understanding of the science and technological aspects of their world. Science areas and curriculum include active learning through individual curiosity, cooperative exploration, and a desire to understand things going on around a classroom and a child’s community. Learning environments with multiple opportunities for preschoolers to explore and manipulate items allow children to formulate a solid foundation of scientific knowledge and the scientific process. When children ask questions and experiment, they are building literacy, vocabulary, communication and math skills.
For more information on the scientific process, watch the following video:
Social Studies
Preschoolers learn about themselves, their family, their school, their community and the greater world as they interact with family members, peers and caring adults. These cooperative interactions allow children to develop, practice and apply skills required to be full participants in a democratic society.
To learn more about social studies in a preschool classroom, please see the following information: http://www.greatschools.org/gk/articles/your-preschooler-and-social-studies/
This link also provides tips to aide in the home-school connection as it offers additional activities that can be done at home.
Assessment
Lesson 5 Discussion
Why is it important to have guidelines available for educators who are teaching preschoolers?
Lesson 5 Quiz
Look at this picture. Use many elements and indicators to describe this snapshot. Justify your choices.
